Blog 3: Creating AWS S3 Bucket
Creating a S3 Bucket
Amazon Simple Storage Service(Amazon S3) is an object storage service that offers industry-leading scalability, data availability, security, and performance. Amazon S3 provides easy-to-use management features so you can organize your data and configure finely-tuned access controls to meet your specific business, organizational, and compliance requirements. Amazon S3 is designed for 99.99999999999% (11 9’s) of durability, and stores data for millions of applications for companies all around the world.
By default, you can create up to 100 buckets in each of your AWS accounts. To create additional buckets, you cna increase your account bucket quota to maximum of 1000 buckets by submitting a service quota increase.
To create a bucket:
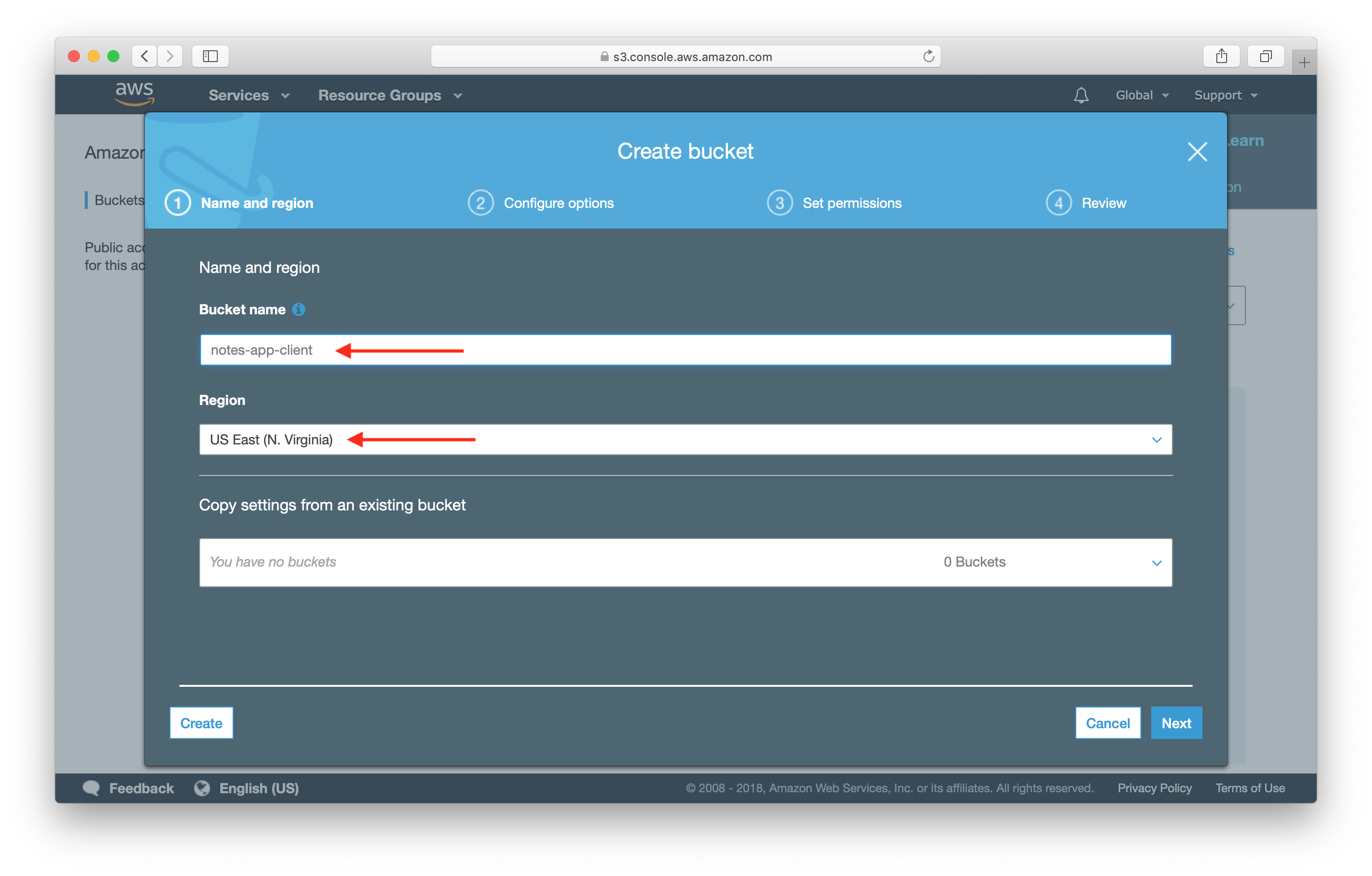
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open Amazon S3 Console
- Choose Create Bucket
- In Bucket name, Enter a DNS-Complaint name for your bucket.
NOTE: When assigning a bucket name, its should be unique across all Amazon S3 Be between 3 and 63 characters long Name should NOT contain UPPERCASE characters Name should start with a LOWERCASE letter or number
- In Region, choosing the AWS Region where you want the bucket to reside. While selecting a Region, we should select region that is closer to you. To reduce the latency and costs and address regulatory requirements.
NOTE: S3 Objects are stored in particular regioon only unless explicitly transferred them to another region.
-
Bucket Settings to block Public Access. It is recommended to leave all settings enabled unless if the user requires to turn one or more of them off for using specific case. EG: hosting a public website. Blocking public access settings that you enable for the bucket will also enable for all access points that you craete on the bucket.
- Advanced Settins
- s3 Object Lock
- Select Create bucket

Click the link below for the AWS documentation for more information:
Creating S3 Bucket using AWS CLI
When creating S3 Bucket using AWS CLI, we have the option to specify the accounts or groups that should be granted specific permissions on the bucket. There are two ways to give permissions using headers.
- By specifying a canned ACL using the x-amz-acl requrest header. Each ACL has a predefined set of grantess and permissions
- By specifying permissions explicitly. EG: x-amz-grant-read, x-amz-grant-write, x-amz-grant-read-acp, x-amz-grant-write-acp, x-amz-grant-full-control headers.
The following command creates a bucket named limbu-bucket:
$ aws s3api create-bucket –bucket limbu-bucket –region us-east-1
Location Constratints outside us-east-1 region
By using the Location Constraint syntax to denote region outside us-east-1:
$ aws s3api create-bucket –bucket limbu-bucket –region us-west-1 –create-bucket-configuration LocationConstraint=us-west-1